This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to examine the strength of the relationships between…


This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to examine the strength of the relationships between…

Book chapter exploring how to communicate about the benefits and risks of vaccination in times of pandemics and uncertainties.

Introducing The Lancet–London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine Commission.

Within weeks of the emergence of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China, misleading rumours and conspiracy theories about the origin circulated the globe paired with fearmongering, racism and mass purchase of face masks, all closely linked to the new ‘infomedia’ ecosystems of the 21st century marked by social media.

The Vaccine Confidence Project™ conducted a systematic scoping review to identify and summarise tools and methodologies that have been used to monitor social media around vaccination.

This systematic review aims to identify the social consequences of mass quarantine during previous and current infectious disease outbreaks and recommended strategies to mitigate the negative social implications of COVID-19 lockdowns.

Vaccination against infectious diseases has changed the future of the human species, saving millions of lives every year, both children and adults, and providing major…

This report outlines the methods and the findings of the VCP’s research, which was conducted to support The Learning Network for Countries in Transition countries in assessing and addressing their vaccine hesitancy issues and in building vaccine confidence capabilities.
Commentary on the importance of focusing on vaccination throughout life.

This year, the World Health Organization named vaccine hesitancy as one of the top 10 global health threats, alongside threats as grave as climate change, antimicrobial…

A qualitative study was conducted to gain a contextualised understanding of factors influencing vaccination acceptance during pregnancy in Hackney, a borough in north-east London,…
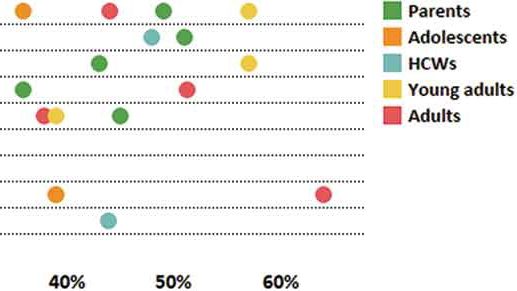
Europe is increasingly described as the region in…
Notifications