This paper explores online communication about vaccines in 2021, offering insights into how positive, and negative, messages spread. The data analysis was conducted by NetBase Quid, an analytics platform, with additional input from the Vaccine Confidence Project at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine.
Related content

The UNICEF Regional Office for Europe and Central Asia (UNICEF ECARO) and the VCP worked in partnership to better understand the impact of social media on caregivers’ attitudes, beliefs, trust, immunisation intention and uptake.

Overview Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, the Vaccine Confidence Project teamed up with YouTube and other health partners to reach people with credible information…

Overview The Vaccine Confidence Project at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, in partnership with Premise, developed ASSURE – Assessing Signals and Supporting Resilience.
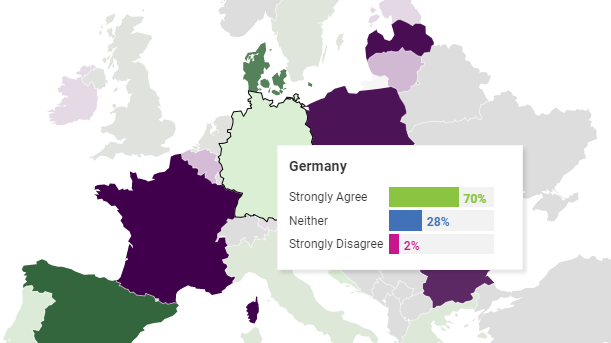
In this study we assessed the overall state of confidence in vaccines among the public in all 27 EU member states.

To identify knowledge gaps, beliefs and attitudes in relation to the COVID-19 pandemic and COVID-19 vaccine acceptance among adults in the Asia-Pacific region, the Vaccine Confidence Project conducted two waves of quantitative research in 2021 and 2022.

In the context of the current communication environment, where online content about vaccination can rapidly be created and shared across the world, media monitoring has become an important tool.